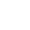Experiment Principle
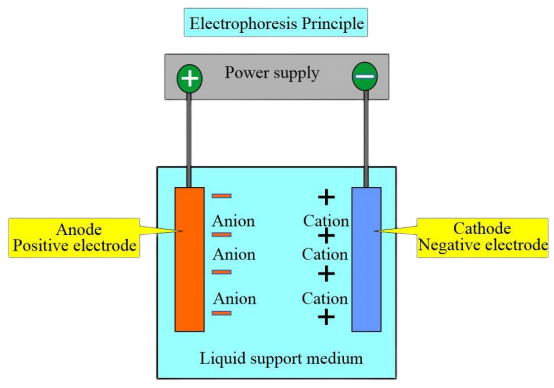
Hemoglobin electrophoresis aims to detect and confirm various normal and abnormal hemoglobins.
Due to the different charges and isoelectric points of different hemoglobin types, in a certain pH buffer solution, when the isoelectric point of hemoglobin is lower than the pH of the buffer solution, hemoglobin carries a negative charge and migrates towards the anode during electrophoresis. Conversely, hemoglobin with a positive charge moves towards the cathode.
Under a certain voltage and after a specific electrophoresis time, hemoglobins with different charges and molecular weights exhibit different migration directions and speeds. This allows for the separation of distinct zones, and subsequent colorimetric or electrophoretic scanning analysis can be performed on these zones to quantify various hemoglobins. The most commonly used method is pH 8.6 cellulose acetate membrane electrophoresis.
Within the cytoplasm, ethylene glycol groups (CHOH-CHOH) present in glycogen or polysaccharide substances (such as mucopolysaccharides, mucoproteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, etc.) are oxidized by periodic acid and converted into aldehyde groups (CHO-CHO). These aldehyde groups combine with the colorless purplish-red Schiff reagent, forming a purple-red dye that deposits where polysaccharides are present in the cell. This reaction is known as periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining, formerly referred to as glycogen staining.
Experiment Method
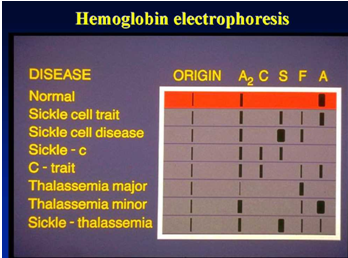
Materials: Cellulose acetate membrane, electrophoresis apparatus(DYCP-38C and power supply DYY-6C ), Superior Sample Loading Tool( pipette), spectrophotometer, colorimetric cuvettes, buffers.
Buffer:
(1) pH 8.6 TEB Buffer: Weigh 10.29 g Tris, 0.6 g EDTA, 3.2 g boric acid, and add distilled water to 1000 ml.
(2) Borate Buffer: Weigh 6.87 g borax and 5.56 g boric acid, and add distilled water to 1000 ml.
Procedure:
Preparation of Hemoglobin Solution
Take 3 ml of blood containing heparin or sodium citrate as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes and discard the plasma. Wash the red blood cells three times with physiological saline (750 rpm, 5 minutes centrifugation each time). Centrifuge at 2200 rpm for 10 minutes and discard the supernatant. Add an equal amount of distilled water, then add 0.5 times the volume of carbon tetrachloride. Shake vigorously for 5 minutes, and then centrifuge at 2200 rpm for 10 minutes to collect the upper Hb solution for later use.
Soaking the Membrane
Cut the cellulose acetate membrane into strips measuring 3 cm × 8 cm. Soak them in pH 8.6 TEB buffer until fully saturated, then remove and blot dry with filter paper.
Spotting
Use a pipette to spot 10 μl of the hemoglobin solution vertically onto the cellulose acetate membrane (the rough side), about 1.5 cm from the edge.
Electrophoresis
Pour the borate buffer solution into the electrophoresis chamber. Place the cellulose acetate membrane with the spotted side at the cathode end of the chamber. Run at 200 V for 30 minutes.
Elution
Cut out the HbA and HbA2 zones, place them in separate test tubes, and add 15 ml and 3 ml of distilled water, respectively. Gently shake to elute the hemoglobin completely, then mix.
Colorimetry
Zero the absorbance using distilled water for the elution solution and measure the absorbance at 415 nm.
Calculation
HbA2(%) = Absorbance of HbA2 tube / (Absorbance of HbA tube × 5 + Absorbance of HbA2 tube) × 100%
Experimental Results Calculation
Reference Range for pH 8.6 TEB Buffer Cellulose Acetate Electrophoresis: HbA > 95%, HbA2 1%-3.1%
Notes
Electrophoresis time should not be too long. The cellulose acetate membrane should not dry out during electrophoresis. Stop electrophoresis when HbA and HbA2 are clearly separated. Prolonged electrophoresis can cause band diffusion and blurring.
Avoid using too much sample. Excessive hemoglobin liquid can lead to band detachment or insufficient staining, resulting in falsely elevated HbA levels.
Prevent contamination of the cellulose acetate membrane with proteins.
The current should not be too high; otherwise, hemoglobin bands may not separate.
Always include specimens from normal individuals and necessary known abnormal hemoglobins as controls.
Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology manufactures the professional electrophoresis tank for hemoglobin electrophoresis that is the model DYCP-38C cellulose acetate membrane electrophoresis tank, and there are two models of electrophoresis power supply available for the cellulose acetate membrane electrophoresis tank DYY-2C and DYY-6C power supply.
Meanwhile, Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology provides cellulose acetate membrane for customers, and the size of cellulose acetate membrane can be customized. Welcome to ask us for samples and more information.
Beijing Liuyi brand has more than 50-year history in China and the company can provide stable and high-quality products all around the world. Through years of development, it is worthy of your choice!
We are now looking for partners, both OEM electrophoresis tank and distributors are welcomed.
If you have any purchasing plan for our products, please don’t hesitate to contact us. You can send us message at email sales@ly.com.cn or sales01@ly.com.cn, or please call us at +86 15810650221 or add Whatsapp +86 15810650221, or Wechat: 15810650221
Post time: Sep-20-2023